A ‘PARASOL’ FOR THE PLANET…
… to mitigate the impacts of climate change?
What can we do if we cannot reduce greenhouse gas emissions sufficiently and Earth’s climate threatens to warm by more than 2°C?
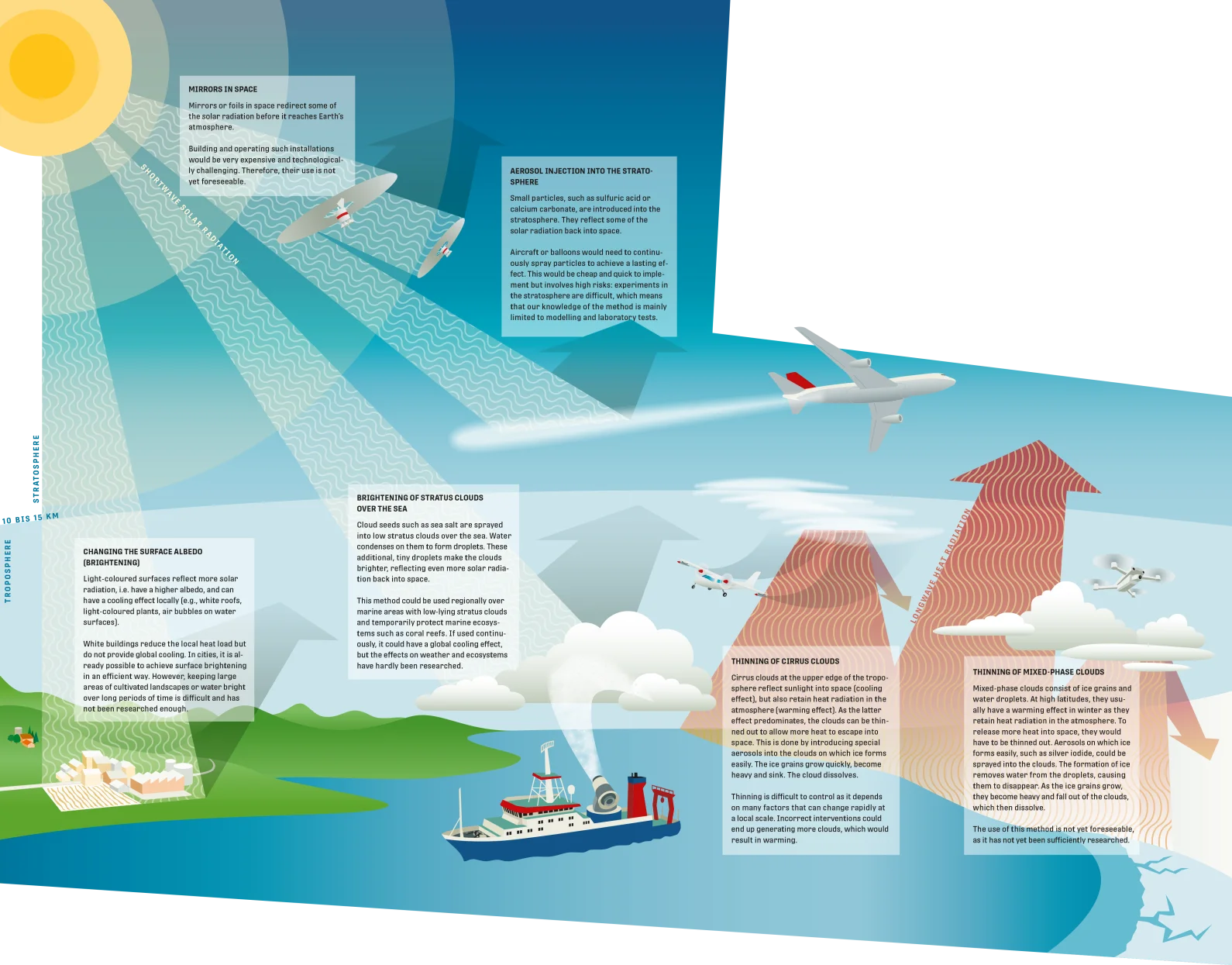
Solar Radiation Modification (SRM)
SRM is a controversial concept. It aims to reduce Earth’s natural warming to counteract the additional temperature rise caused by climate change. One approach is to reflect more solar radiation back into space, while another is to allow more heat radiation from Earth’s surface to escape into space.
CHALLENGES
SRM would not tackle the actual driver of human-caused warming: the excessive concentrations of greenhouse gases. Nor would it alleviate associated consequences, such as ocean acidification. However, SRM could buy us time to further reduce emissions, develop CO₂ removal technologies and prevent critical climate tipping points from being crossed. Some SRM methods could already be implemented. However, they carry unforeseeable and under-researched risks for weather, the ozone layer and the health of living organisms and ecosystems. Moreover, use followed by a sudden halt of SRM methods could lead to rapid warming.
In addition to major ethical concerns, international coordination and regulation would be complex: not all regions of the world would benefit equally, and it is unclear who would decide on the use of SRM or be liable for it. The scientific community is divided on whether SRM should be further researched, as it could lower the motivation to reduce emissions.